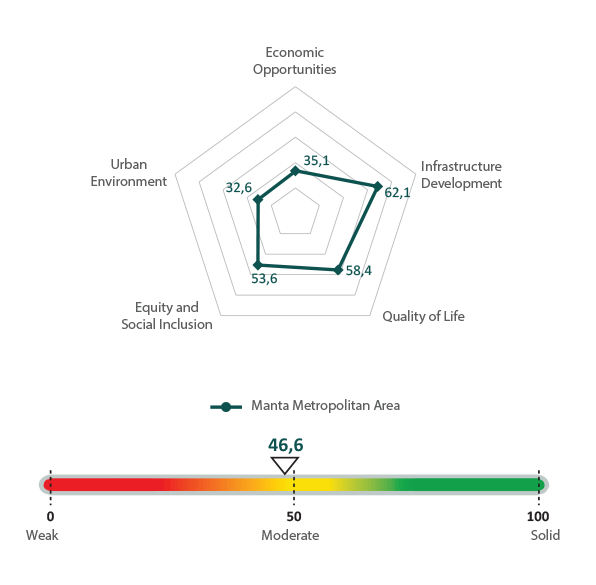
According to a reading of the levels of territorial prosperity in the Metropolitan Area of Manta (Manta, Montecristi and Jaramijó cantons), a moderately weak value of territorial prosperity is presented according to the Urban Prosperity Index (CPI) with 46.6 points above 100. The main strength of the territory is the dimension of infrastructure development, with results in housing and public services scoring a solid moderate. Likewise, the dimensions of quality of life and equity and social inclusion stand out, with a moderate-solid rating that shows the need to reinforce urban policies, plans and strategies that strengthen health services, education and accessibility to public spaces, as well as the security and protection necessary to enjoy these.

The results of these indicators show that, among the main challenges for prosperity, it is necessary to strengthen the provision of social infrastructure, which results in a very weak range, with only 0.24 libraries per 100,000 inhabitants (out of an expected range of between 1 and 7 libraries) and 1.93 doctors per thousand people (the ideal range is between 5 and 7). Similarly, internet access (53.76% of the inhabitants have internet and less than a fourth access to computers 23.28%) and its quality show the need to prioritize policies and programs that improve information and communication technologies , starting with the monitoring of the band speed available in the territory (27.4 Mbps for Ecuador).
Infrastructure for development measurement results: 62.1 / 100
The results of these indicators show that, among the main challenges for prosperity, it is necessary to strengthen urban government policies and tools to generate a more sustainable energy matrix, protect strategic resources and provide the necessary incentives and conditions for waste treatment. liquids and solids.
Environmental measurement results: 62.1 / 100


The results of these indicators show that, among the main challenges for prosperity, there is evidence of the need to strengthen the health and education systems in the territory, as well as the provision and accessibility of public spaces. Health and education conditions in the territory show a moderately weak level, with a life expectancy at birth of 72 years and a relatively low infant mortality rate (11.2 per 1000 live births, with 2.2 infants being the ideal reference value). In terms of education, the literacy rate is 93%, however, there is a significant challenge in the enrollment rate in higher education (17%).
Quality of life measurement results: 58.4 / 100
The results of these indicators show that, among the main challenges for prosperity, it is necessary to reinforce urban policies that strengthen the local economy, taking advantage of existing economies of agglomeration to generate quality employment and offer economic opportunities for its inhabitants. In this way, it is expected that the informal employment rate will be reduced by 39% of the population who have incomes below the minimum wage.
Economic opportunities measurement results: 35.1 / 100


The results of these indicators show that, among the main challenges for prosperity, it is necessary to reinforce economic inclusion policies that at the same time aim to reduce the distance between income extremes, as well as generate job offer and livelihoods for young people, with special emphasis on young women. Likewise, it is necessary to promote equitable access to education for women, who currently have a rate of 0.78 women for every man enrolled in an educational institution in secondary education.
Equity and social inclusion measurement results: 53.6 / 100
The results of these indicators show that, among the main challenges for prosperity, the promotion of citizen participation through Neighborhood Boards and other intervention mechanisms in decision-making processes is required, since no data was known about people belonging to community organizations. Likewise, the strengthening of the own income collection system, accompanied by the formalization and registration of companies that allow exceeding the participation of local collection in the entire budget (currently it is 49.9%).
Urban governance and legislation measurement results: 58.4 / 100
